Hamza Asumah, MD, MBA
In recent years, the healthcare industry has been undergoing a significant transformation driven by the shift towards value-based care. This paradigm emphasizes delivering high-quality care at lower costs, focusing on patient outcomes and satisfaction rather than the volume of services provided. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, effective leadership plays a crucial role in driving this transformation and ensuring the success of value-based care initiatives.
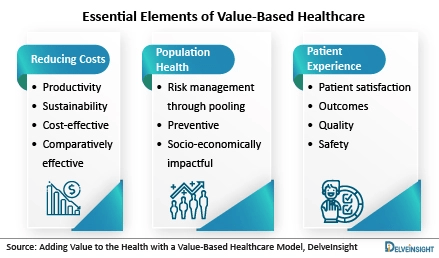
Photo By Delve Insight
Understanding Value-Based Care
Value-based care is a model that seeks to align financial incentives with the quality and efficiency of healthcare services. Unlike the traditional fee-for-service model, which rewards healthcare providers based on the volume of services they deliver, value-based care emphasizes outcomes, efficiency, and patient satisfaction. By incentivizing providers to deliver high-quality care that leads to better patient outcomes and experiences, value-based care aims to improve the overall health of populations while reducing healthcare costs.
Key Components of Value-Based Care
Several key components define value-based care:
1. Patient-Centered Care: Value-based care puts patients at the center of the healthcare experience, focusing on their needs, preferences, and outcomes. By engaging patients in their care decisions and providing personalized, coordinated care, healthcare providers can improve patient satisfaction and health outcomes.
2. Population Health Management: Value-based care emphasizes managing the health of populations rather than just treating individual patients. By analyzing data and identifying high-risk patients, healthcare organizations can proactively address health issues, prevent complications, and reduce costs.
3. Quality and Performance Metrics: Value-based care relies on robust quality and performance metrics to measure the effectiveness of care delivery. By tracking key indicators such as readmission rates, patient satisfaction scores, and adherence to best practices, healthcare organizations can identify areas for improvement and drive better outcomes.
4. Care Coordination and Integration: Value-based care promotes care coordination and integration across different healthcare settings and providers. By breaking down silos and improving communication among care teams, healthcare organizations can deliver seamless, efficient care that meets patients’ needs.
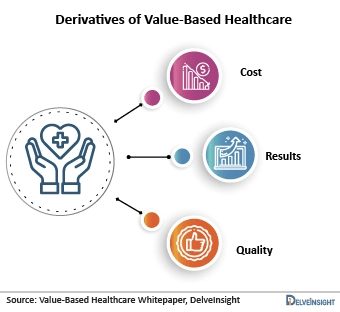
Photo By Delve Insight
The Role of Leadership in Driving Transformation
Effective leadership is essential for driving the transformation to value-based care and achieving its goals of improving patient outcomes and reducing costs. Leaders in healthcare organizations must possess the following qualities to successfully navigate this shift:
1. Vision and Strategy: Leaders need to have a clear vision of the organization’s goals and a strategic plan for transitioning to value-based care. By setting goals, aligning stakeholders, and communicating effectively, leaders can inspire their teams to embrace change and work towards common objectives.
2. Data-Driven Decision-Making: Value-based care relies on data and analytics to measure performance, identify opportunities for improvement, and drive decision-making. Leaders should champion a data-driven culture within their organizations, investing in technology and resources to collect, analyze, and act on data effectively.
3. Collaboration and Communication: Transforming healthcare delivery requires collaboration and communication among diverse stakeholders, including clinicians, administrators, payers, and patients. Leaders must foster a culture of teamwork, transparency, and open communication to ensure alignment and engagement across the organization.
4. Change Management and Innovation: Transitioning to value-based care involves significant changes in processes, workflows, and mindsets. Leaders must be adept at change management, guiding their teams through transitions, overcoming resistance, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
5. Patient-Centered Focus: At the core of value-based care is a focus on delivering patient-centered care that improves outcomes and experiences. Leaders must prioritize patient needs and preferences, and empower their teams to provide compassionate, personalized care that meets the highest standards of quality and safety.
6. Financial Acumen: Value-based care requires a shift from volume-based reimbursement to alternative payment models that reward quality and outcomes. Leaders must have a strong understanding of financial principles, revenue models, and risk-sharing arrangements to navigate the financial complexities of value-based care and ensure the sustainability of their organizations.
7. Continuous Learning and Development: The healthcare landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies, best practices, and regulations shaping the industry. Leaders must commit to continuous learning and professional development, staying abreast of industry trends, innovations, and evidence-based practices to drive continuous improvement and stay ahead of the curve.

Photo By SHRM
Strategies for Driving Value-Based Leadership
To drive value-based leadership and transform healthcare delivery, leaders can adopt the following strategies:
1. Establish a Clear Vision: Articulate a clear vision for value-based care that aligns with the organization’s mission and values. Communicate this vision to all stakeholders and inspire a shared sense of purpose and direction.
2. Foster a Culture of Accountability: Hold teams accountable for delivering high-quality, cost-effective care that meets performance metrics and patient outcomes. Establish a culture of accountability, transparency, and continuous improvement to drive results.
3. Invest in Technology and Analytics: Leverage technology and data analytics to measure performance, track outcomes, and identify opportunities for improvement. Invest in electronic health records, population health management tools, and predictive analytics to support value-based care initiatives.
4. Engage Patients and Providers: Involve patients and providers in care decisions, treatment planning, and goal setting. Foster strong relationships with patients, empower them to take an active role in their care, and support providers in delivering coordinated, patient-centered care.
5. Collaborate with Payers and Partners: Collaborate with payers, community organizations, and other healthcare providers to improve care coordination, share best practices, and align incentives for value-based care. Build partnerships that support population health management and enhance the continuum of care.
6. Measure and Monitor Performance: Establish key performance indicators and quality metrics to track progress towards value-based care goals. Monitor performance regularly, identify areas for improvement, and take proactive steps to address gaps and drive better outcomes.
7. Empower and Develop Leaders: Invest in leadership development programs, mentorship opportunities, and training initiatives to empower leaders at all levels of the organization. Cultivate a pipeline of future leaders who embody the values of value-based care and can drive transformational change.

Photo By Mckinsey
Transforming healthcare delivery through value-based leadership is essential for improving patient outcomes, reducing costs, and enhancing the overall quality of care. By embracing the principles of value-based care, fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration, and empowering leaders to drive change, healthcare organizations can navigate the complexities of the evolving healthcare landscape and deliver high-value, patient-centered care that meets the needs of populations. Effective value-based leadership is not just a strategic imperative—it is a moral imperative that requires a commitment to excellence, compassion, and continuous improvement in healthcare delivery.
Please leave your comments below

Leave a comment