Hamza Asumah, MD, MBA
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital health solutions worldwide, and Africa has not been an exception. Telemedicine, once a niche service, has now become a critical component of healthcare delivery across the continent. This blog post will explore the emergence and trend of telemedicine health companies in Africa post-pandemic, with an examination of successful and unsuccessful companies, common causes of failure, and practical strategies for success.
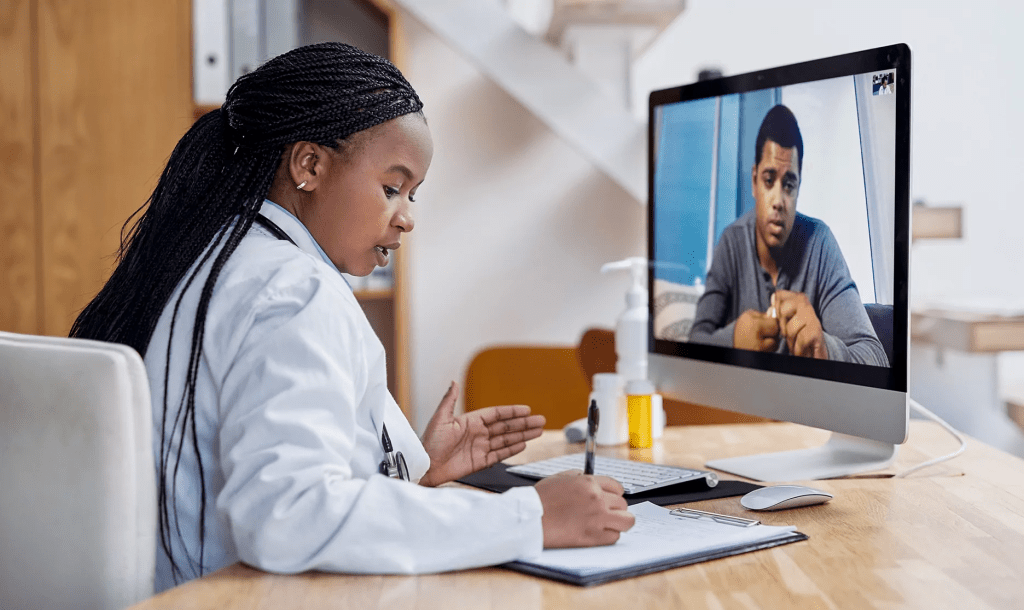

Photo By Baker College
While comprehensive, up-to-date data on technology adoption in Africa is difficult to come by, various studies and reports provide insights into the current state of technology penetration and the predicted trends for the next decade.
1. Internet penetration: As of 2021, Africa’s internet penetration rate was around 47%, with over 590 million people having access to the internet (source: Internet World Stats). This represents significant growth compared to 2005 when the internet penetration rate was just 2%. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) predicts that internet penetration will continue to increase in Africa, reaching 60% of the population by 2030.
2. Mobile phone adoption: Mobile phone adoption has skyrocketed in Africa over the past two decades. According to the GSMA, there were approximately 1.2 billion mobile connections in Africa in 2021, with a unique subscriber base of over 520 million. The GSMA expects the number of unique mobile subscribers to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% over the next five years, reaching approximately 634 million by 2025.
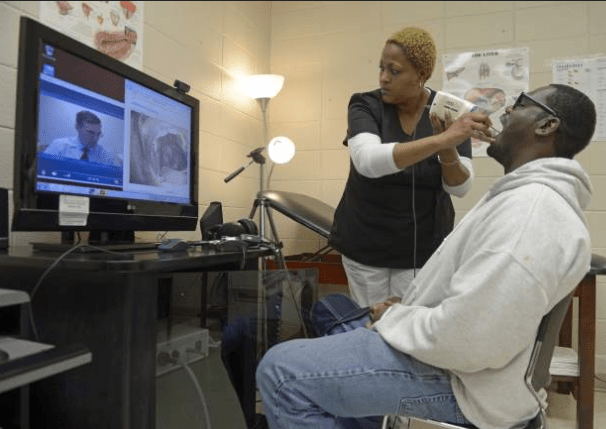
Photo By Space In Africa
3. Smartphone adoption: Smartphone adoption has also been growing rapidly in Africa. In 2021, there were an estimated 300 million smartphone users on the continent (source: Statista). This number is expected to reach around 678 million by 2025, according to the GSMA.
4. E-commerce: E-commerce in Africa is experiencing significant growth, fueled by increasing internet and smartphone penetration. In 2020, the e-commerce market in Africa was valued at around $20 billion (source: Statista). The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 21.4% between 2021 and 2028, reaching a value of $116.4 billion by 2028 (source: Grand View Research).
5. Digital financial services: Mobile money and digital financial services have seen widespread adoption in Africa, particularly in countries like Kenya, where M-Pesa has become a household name. As of 2020, there were approximately 300 million mobile money accounts in Africa, with a total transaction value of $490 billion (source: GSMA). The growth of digital financial services is expected to continue, driven by increased smartphone adoption and supportive government policies.
6. Renewable energy and smart grid technology: Africa has immense potential for renewable energy generation, and the adoption of smart grid technology is expected to increase in the coming years. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), renewable energy capacity in Africa is expected to increase from 58 GW in 2019 to around 310 GW by 2030.
Photo By JHU Hub
Emergence and Trend of Telemedicine in Africa
The number of telemedicine start-ups in Africa has increased significantly in recent years, particularly in response to the pandemic. According to a recent study, there are now over 200 telemedicine companies operating across the continent, with Nigeria, South Africa, and Kenya leading the charge. These companies offer a range of services, including remote consultations, diagnostics, and medication delivery.
Successes and Failures in African Telemedicine
While some telemedicine companies have experienced rapid growth and success, others have struggled to gain traction.
A few notable successes include:
1. Helium Health (Nigeria): A leading electronic medical records and telemedicine provider that has expanded its services to several African countries, including Kenya, Ghana, and Liberia.
2. mPharma (Ghana): A digital health platform that connects patients, pharmacies, and healthcare providers, enabling more efficient delivery of pharmaceutical services.
3. Babyl (Rwanda): A digital health company that provides teleconsultations, prescriptions, and lab test referrals via mobile phones.
On the other hand, some companies have struggled to achieve the same level of success. Common factors contributing to failure include:
1. Insufficient funding: Many telemedicine start-ups face capital constraints, limiting their ability to scale and invest in technology and infrastructure.
2. Limited internet connectivity: While internet access is improving across Africa, there are still areas with limited connectivity, making it difficult for telemedicine companies to serve remote populations.
3. Resistance to adoption: Some healthcare providers and patients may be hesitant to embrace telemedicine due to concerns about the quality of care, data privacy, and the loss of face-to-face interaction.

Photo By News Medical
Strategies for Success
For telemedicine companies looking to succeed in the African market, the following strategies should be considered:
1. Develop partnerships with local healthcare providers: By working closely with existing healthcare providers, telemedicine companies can build trust, share resources, and ensure that their services complement, rather than compete with, traditional care.
2. Focus on user experience and accessibility: Telemedicine services should be easy to use, with user-friendly interfaces and support for a variety of devices and internet speeds. In addition, companies should invest in local language support and culturally sensitive content.
3. Leverage mobile technology: With the widespread adoption of mobile phones in Africa, telemedicine companies should prioritize developing mobile-first solutions that are accessible to a broad range of users.
4. Invest in education and awareness campaigns: Increasing public awareness and understanding of the benefits of telemedicine can help drive adoption and overcome resistance to change.
5. Secure funding and financial sustainability: Telemedicine companies should explore various funding sources, including grants, angel investments, and partnerships with larger healthcare organizations. Additionally, developing sustainable revenue models is essential for long-term success.
As the adoption of telemedicine continues to grow, it will be important for governments, healthcare providers, and entrepreneurs to work together to create a supportive environment for innovation and to ensure that these services meet the diverse needs of Africa’s population. By doing so, they can contribute to a brighter, healthier future for the continent.
Photo By TELUS International
The Future of Telemedicine and the Role of AI
Telemedicine has already made significant strides in improving access to healthcare, particularly in remote and underserved areas. As technology continues to advance, we can expect telemedicine to evolve and become even more integrated into our daily lives. Here are some predictions for the future of telemedicine and the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in offering a competitive advantage:
1. Integration of telemedicine into mainstream healthcare: Telemedicine is likely to become an integral part of healthcare systems around the world. As more people become accustomed to using digital health solutions, healthcare providers will increasingly rely on telemedicine for routine consultations, follow-up appointments, and even the management of chronic conditions.
2. Expansion of telemedicine services: In the future, telemedicine platforms may offer a wider range of services, including mental health support, preventive care, and personalized medicine. This expansion will enable patients to access more comprehensive care through a single platform, making healthcare more efficient and convenient.

Photo By AFR-IX Telecom
3. AI-driven diagnostics and treatment recommendations: AI algorithms can analyze medical data, such as patient records, lab results, and imaging data, to provide more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment recommendations. This can help healthcare providers make more informed decisions and improve patient outcomes.
4. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants: AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can provide patients with instant access to medical information and advice, helping to triage symptoms, answer general health questions, and even offer mental health support. This can free up healthcare professionals to focus on more complex cases and enable patients to receive timely care without needing to visit a clinic or hospital.
5. Enhanced remote patient monitoring: AI-driven systems can analyze data from wearable devices and connected medical equipment to monitor patients’ vital signs, detect anomalies, and alert healthcare providers to potential issues. This can enable more proactive and preventive care, particularly for patients with chronic conditions.
6. Improved medical education and training: AI-driven simulation and virtual reality tools can help medical professionals hone their skills and access up-to-date information on best practices and emerging treatments. This can lead to a more skilled and informed healthcare workforce.
7. Streamlined administrative tasks: AI can help automate various administrative tasks, such as scheduling appointments, managing patient records, and processing insurance claims. This can reduce the burden on healthcare providers and allow them to focus more on patient care.
8. Cross-border telemedicine: As telemedicine becomes more widely accepted, we may see an increase in cross-border care, allowing patients to access specialist consultations and treatment from healthcare providers in other countries. This can help address the shortage of medical experts in certain regions and ensure that patients receive the best possible care.

Photo By Sci Dev
The future of telemedicine looks promising, with AI playing a pivotal role in enhancing healthcare delivery and offering a competitive advantage to telemedicine providers. By harnessing the power of AI, telemedicine can become more efficient, accessible, and personalized, ultimately improving patient outcomes and transforming the way we access healthcare services around the world.
Telemedicine has the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery in Africa, making quality care more accessible to millions of people. While there have been successes and failures in the African telemedicine landscape, the key to long-term success lies in understanding the unique challenges faced by the continent and implementing practical strategies to overcome them. By forging strong partnerships with local healthcare providers, focusing on user experience and accessibility, leveraging mobile technology, investing in education and awareness campaigns, and securing funding and financial sustainability, telemedicine companies can position themselves for success in Africa’s rapidly evolving digital health ecosystem.
Please leave your insights in the comment section below,

Leave a comment