Hamza Asumah, MD, MBA
In recent years, health information tools have become essential components in transforming the quality of healthcare services and improving clinical practice across the globe. For doctorpreneurs in Africa, leveraging these tools is vital for building successful hospital businesses, enhancing patient care, and driving the growth of the healthcare industry.
Health information systems (HIS) are systems that are designed to manage, store, analyze, and report on health-related data. These systems can include electronic health records (EHRs), health management information systems (HMIS), and other digital tools that help healthcare providers and public health officials collect, manage, and use health data.
Photo By E Health Magazine
Several studies have demonstrated the positive impact of health information tools on clinical practice efficiency and healthcare business growth. Some key findings include:
– A study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research found that the implementation of EHRs in a Nigerian hospital resulted in a 12% increase in outpatient visits and a 15% increase in inpatient admissions, suggesting improved efficiency and service quality.
– A World Health Organization report on telemedicine in Africa highlighted its potential to increase access to healthcare services, particularly in rural areas, and to facilitate consultations with specialists, leading to better patient outcomes.
– A systematic review published in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association found that clinical decision support systems can reduce diagnostic errors by up to 50% and improve treatment plan adherence by over 30%.
– A study published in the Journal of Health Informatics in Developing Countries found that the implementation of HIEs in Ethiopia led to a 10% reduction in hospital readmissions and a 7% decrease in emergency department visits, indicating improved care coordination and resource utilization.
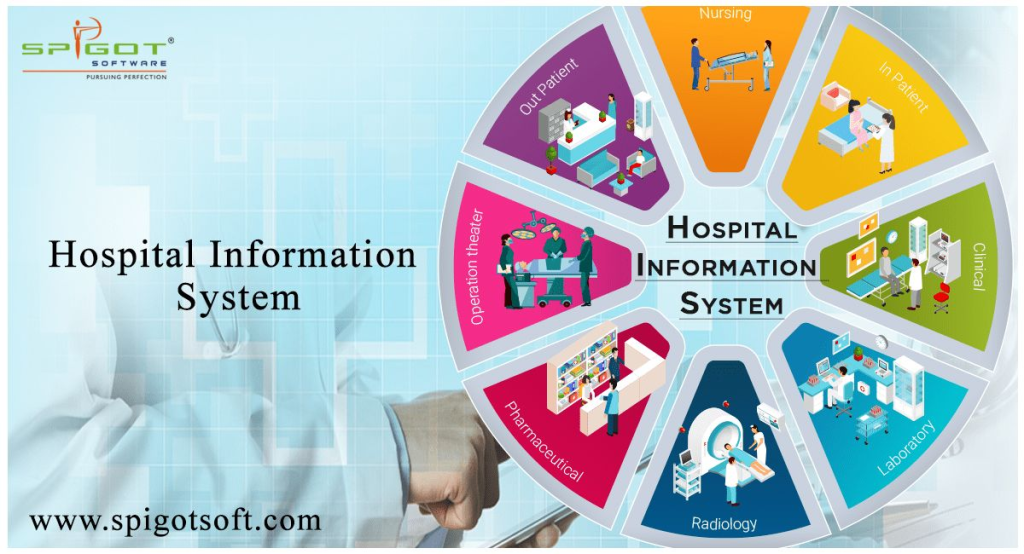
Photo By Pinterest
In Africa, there are several health information systems that can be used effectively, despite the infrastructure challenges faced by the continent. Some of these systems include:
1. Mobile health (mHealth) systems: These systems use mobile phones and other mobile devices to collect and transmit health data. They can be used to support health workers in remote or hard-to-reach areas, and can also be used to provide health education and support to patients.
2. OpenMRS: OpenMRS is an open-source EHR system that is designed to be flexible and adaptable to the needs of different healthcare settings. It can be customized to meet the specific needs of healthcare providers in Africa, and can be used to manage patient data, support clinical decision-making, and monitor public health trends.
3. DHIS2: DHIS2 is a web-based HMIS system that is widely used in Africa. It can be used to collect and analyze health data, and can be customized to meet the specific needs of different healthcare settings. DHIS2 can be used to support disease surveillance, monitor health outcomes, and track health system performance.
4. CommCare: CommCare is a mobile data collection platform that can be used to support community health workers in collecting and transmitting health data. It can be used to support a wide range of health interventions, including maternal and child health, HIV/AIDS, and malaria.
5. Telemedicine systems: Telemedicine systems use digital technologies to enable remote consultations between healthcare providers and patients. They can be used to support healthcare delivery in areas where there are few healthcare providers, and can also be used to provide specialist care to patients in remote areas.
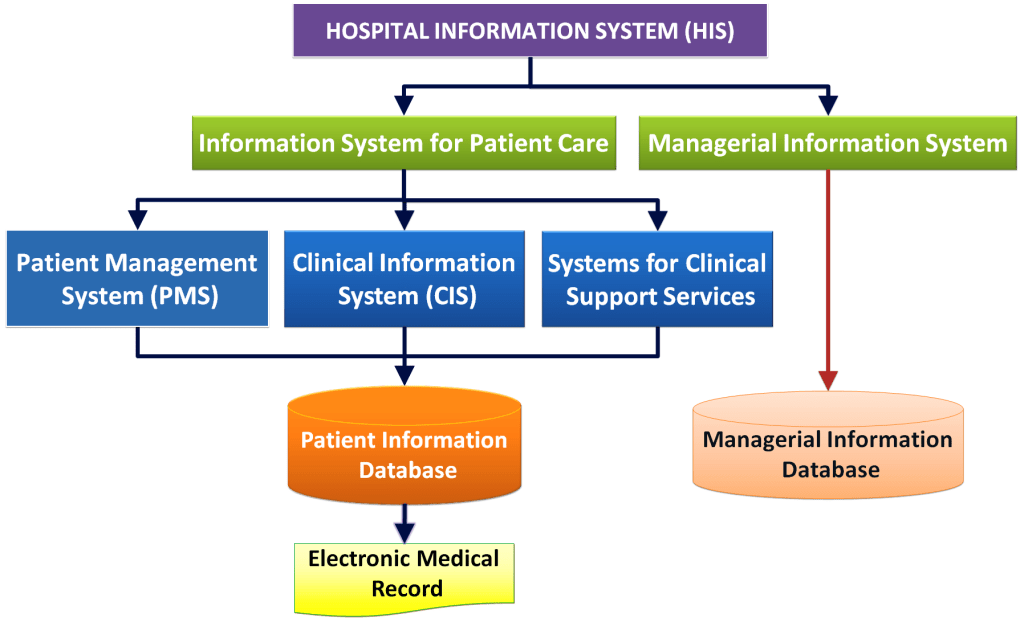
Photo By Healthcare Service Delivery
The adoption rate and trend for health information systems (HIS) in Africa over the last 10 years has been mixed. While there has been progress in the adoption and implementation of HIS in some countries, there are still significant challenges that need to be addressed in order to fully leverage the potential of these systems.
The adoption rate of HIS in Africa has varied by country and by type of system. For example, some countries have made significant progress in implementing electronic health records (EHRs) and health management information systems (HMIS), while others have focused more on mobile health (mHealth) systems and other digital tools.
One trend that has emerged in recent years is the increasing use of open-source HIS solutions in Africa. Open-source HIS solutions, such as OpenMRS and DHIS2, are often more affordable and adaptable to local needs than proprietary solutions, making them a popular choice in low-resource settings.
Another trend has been the growing emphasis on interoperability between different HIS systems. Interoperability allows different systems to share data and communicate with each other, which can help to improve the quality and efficiency of healthcare services.
Despite these positive trends, there are still significant challenges that need to be addressed in order to fully leverage the potential of HIS in Africa. These challenges include limited funding and resources, inadequate infrastructure (such as unreliable electricity and internet connectivity), and a shortage of skilled personnel to manage and use these systems. Additionally, there is a need for better coordination and collaboration among stakeholders in the development and implementation of HIS in Africa.
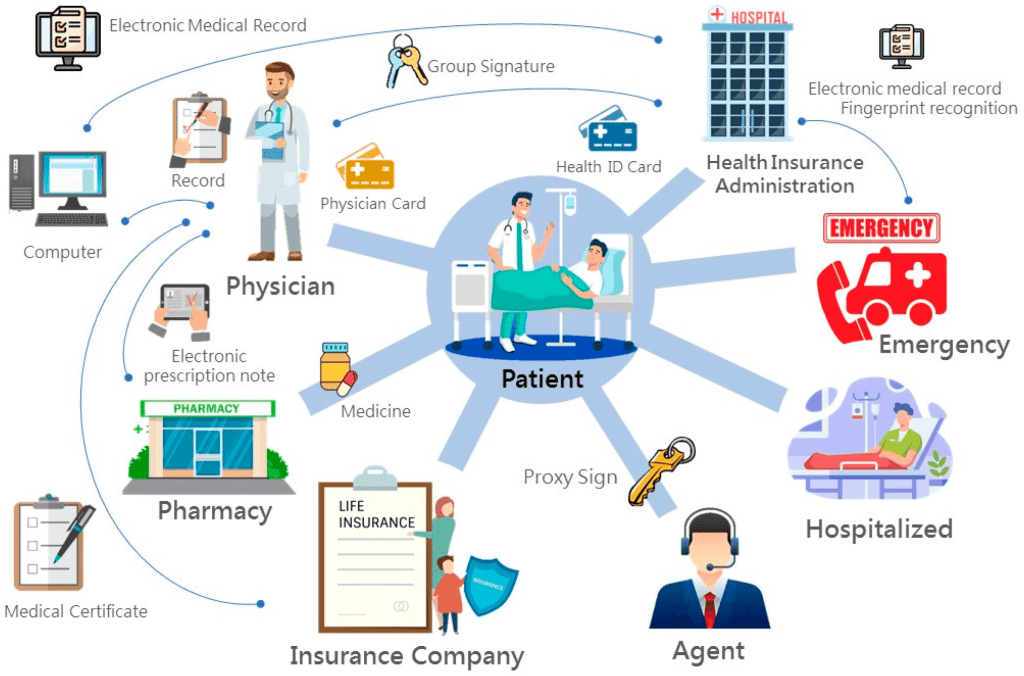
Photo By MDPI
Using Health Information Tools for Improved Clinical Practice
1. Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
EHRs are digital versions of patients’ medical records, which can be accessed and updated by authorized healthcare professionals. Implementing EHRs can help doctorpreneurs streamline their clinical practice by:
– Reducing errors and improving patient safety through better documentation and data sharing
– Enhancing decision-making with access to comprehensive patient information
– Facilitating efficient coordination between healthcare providers
– Improving patient engagement and satisfaction
2. Telemedicine
Telemedicine enables healthcare providers to connect with patients remotely, using video conferencing or other communication technologies. This tool can be incredibly beneficial for doctorpreneurs in Africa by:
– Extending healthcare services to underserved populations
– Reducing the burden on hospitals and clinics
– Providing patients with more convenient and cost-effective care
– Facilitating consultations with specialists and improving patient outcomes
3. Decision Support Systems
Decision support systems use artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to analyze patient data and provide evidence-based recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Incorporating decision support tools can help doctorpreneurs:
– Enhance the quality of care provided by reducing diagnostic errors
– Improve efficiency by minimizing unnecessary testing and treatments
– Facilitate personalized medicine by tailoring treatment plans to individual patients
4. Health Information Exchange (HIE)
HIEs facilitate the secure sharing of patient information among healthcare providers, helping to improve care coordination and reduce duplicative services. Doctorpreneurs can benefit from participating in HIEs by:
– Enhancing clinical decision-making with access to a more comprehensive patient history
– Reducing administrative burdens and healthcare costs
– Improving patient satisfaction by minimizing delays in care

Photo By Software Suggest
These systems can be effective in Africa because they are designed to be flexible and adaptable to the needs of different healthcare settings. They can also be used to support healthcare delivery in areas where there are few healthcare providers, and can help to improve the quality and accessibility of healthcare services. However, it is important to note that the effectiveness of these systems will depend on a range of factors, including the availability of infrastructure (such as reliable internet connectivity), the skills and capacity of healthcare workers, and the level of investment in health information systems.
Please leave your insights in the comment section below.

Leave a comment